
Heart attack is defined as a medical condition when there is an imbalance between the demand and supply of blood flow to the heart. Blood is the source through which the heart muscle gets their oxygen and necessary nutrients, thus their scarcity in case of blockage in the vessels supplying the heart can cause a heart attack.
Most commonly, heart attack occurs when there is an acute occlusion or critical narrowing in the arteries which supply the heart. More often than not, there is a plaque (pre-existing blockage) in the coronary artery, whose surface gets eroded and an acute clot forms on the same and this causes abrupt closure on the passage of blood through the coronary (heart) artery and thus causes the heart attack.
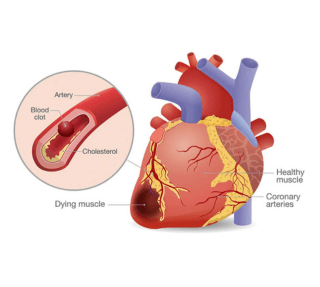
People often use the terms heart attack and cardiac arrest interchangeably. Heart attack means the blood supply through a coronary artery to the heart muscle is diminished or stopped leading to changes in ECG and symptoms of chest pain or breathlessness. Whereas, cardiac arrest is a condition wherein the heart function stops altogether, i.e. the heart stops beating completely.
Though, one of the most common reasons for a cardiac arrest is a heart attack. Treatment for heart attack is to open up the coronary artery in the form of emergency angioplasty or giving blood thinning medications, whereas for cardiac arrest, the treatment is CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) with or without DC cardioversion (electric shocks) and then to treat the underlying cause of cardiac arrest.
Common Symptoms
Atypical Symptoms (Especially in Women, Elderly, and Diabetic patients)
Main Cause
Coronary Artery Disease
Risk Factors
Initial assessment and stabilization. Medications, mainly blood thinning medicines and injections (e.g., Thrombolytics, Antiplatelets).
Emergency Angioplasty (PTCA) with stent insertion. In this procedure, the patient is taken to the cath lab in emergency. A catheter is passed from either the arteries of the wrist or the groins and into the coronary (heart) arteries. Subsequently a contrast agent is injected in to same to identify any blockages in these arteries and once confirmed it is treated subsequently with dilation with balloon inflation and then putting a stent to keep these arteries stretched open.
Coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), if needed at a later date. This is a form of open heart surgery and is needed if a patient has multiple blockages in the coronary artery and also in those cases which are less attractive for PTCA.
Heart attack is one of the most common causes of death and thus its timely early intervention is critical, not only to save life, but also to preserve the heart function to the best possible extent in the long run as well.
The most important hurdle in the treatment of heart attack is its identification, thus any symptoms of chest pain or heartburn should not be neglected and the patient should be taken to the nearest hospital to get the ECG and primary evaluation done.
Once confirmed with a heart attack, the medications should be given immediately and emergency angioplasty should be done. Post procedure, ICU care is essential for recovery and time for recuperation at home is needed as well. Strict adherence to medicines and modification of lifestyle is needed to ensure better long term benefits to the patients. Lifelong follow up with cardiologists is mandated, as a heart attack patient is a heart patient for life.
Many men ignore early cardiac symptoms — until it’s too late. In this video, Dr. Ankur Phatarpekar, Interventional Cardiologist at HVS Hospitals, outlines the most common heart health mistakes men make — and how to prevent them.

