
Medically Reviewed By Dr. Meghav Shah Updated on November 28, 2024
Coronary angioplasty or percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure done to treat blockages or narrowings in the arteries of the heart. It is done commonly via the wrist (radial artery) or through the groins (femoral artery).
The purpose of this procedure is to relieve the narrowings in the coronary artery by balloon dilation and subsequent deployment of stents. This treatment of the narrowings enables better and smooth flow of blood through these arteries and into the heart muscles.
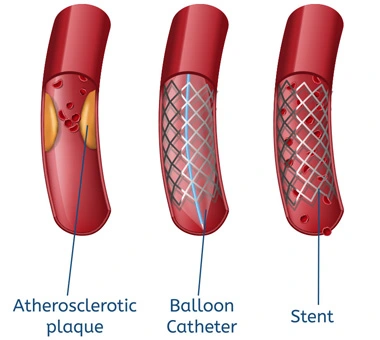
Angioplasty is a generic term used to treat atherosclerotic narrowings in the arteries of our body or occasionally some narrowings in the veins, by means of dilation of same with a balloon catheter and if need be put in a stent i.e. a metallic scaffolding in its place.
Thus angioplasty can be done for the heart arteries, in the brain arteries, renal arteries, peripheral limb arteries or veins etc.
Emergency Coronary Angioplasty (PAMI)
PAMI or primary angioplasty in myocardial infarction is an emergency, life-saving procedure done to treat STEMI (ST elevation myocardial infarction) or acute heart attacks. In this the patients upon diagnosing this condition are immediately taken up in the cath lab, angiography is performed to diagnose the blocked artery and immediate angioplasty is performed to relieve the blockage.
Planned Angioplasty
Patient and the relatives are explained about the procedure and proper consent is taken. Pre-procedure injections are given and the patient is shifted to the cardiac cath lab. Angiography is performed normally via a sheath in the wrists i.e. radial artery or the groins i.e. the femoral artery. This procedure is normally done under local anaesthesia only.
In the cath lab, the patient normally lies flat and a catheter is inserted through the sheath. The catheter passes through the arteries and into the mouth of the coronary i.e. the heart arteries and dye is injected through it with a camera over the patient taking pictures of the heart arteries.
Post the angiogram, we discuss the need for further treatment depending on the findings. If the arteries have significant lesions or blockages, then we could proceed with angioplasty i.e. balloon dilation of the lesion and then further putting in stents.
Once angiography confirms the need for angioplasty, we proceed with the same.
With the modern advancements, more and more difficult cases can be dealt with angioplasty and open heart surgery can be avoided.
Some advances in angioplasty to name a few are as follows -
Once angiography confirms the need for angioplasty, we proceed with the same.
Indications to perform an angioplasty are mainly elective and emergency.
If a patient is having an acute heart attack, an urgent angiography is done to diagnose the occluded artery with the intention to open it up in the form of angioplasty and putting in stents.
If a patient complains of symptoms of chronic stable angina, then an elective angiography can be done if symptoms are refractory to medicines. Based on the angiography findings, the decision can be taken to undergo angioplasty or consider CABG (coronary artery bypass grafting) i.e. open heart surgery.
Diagnostics
Prior to proceeding with angioplasty, it is prudent to get as much information as possible about the heart function. Patients' symptoms are the most important in deciding the line of management. In forms of other investigations, ECG (electrocardiogram), ECHO (echocardiogram), Stress test and angiogram are essential in decision making and planning the angioplasty procedure.
Immediate Post-Procedure Care
Patients are usually shifted to the ICU post procedure to observe for any chest pain or ECG changes. Local site i.e. the radial site or femoral site, from where the procedure is performed is monitored. Blood thinning medicines and injections are given as needed.
Medication Regimen and Lifestyle Changes
It is very important to know that medicines and lifestyle play an equally important role in coronary artery disease. Long term outcomes of angioplasty or CABG are very much dependent on the compliance of medicines and adopting changes in lifestyle which includes a good balanced diet and exercise regimen.
Rehabilitation Programs and Follow-Up Visits
For recuperating from heart disease post the procedure, we offer curated rehabilitation programs that help patients to get back to their routine life sooner. There is good evidence that patients who religiously enrol in rehabilitation programs tend to do well in the long term as compared to patients who opt out of it.
We usually advise patients to come for follow-up a week and then one month post procedure. Thereafter we see them every 3 months for the 1st year and then bi-yearly follow up throughout life. Some blood tests, ECG, and ECHO may be advised on follow-ups as needed. Some patients may be asked to come for follow-ups more frequently depending on the findings by the doctors or if the patients are symptomatic.
Coronary angioplasty offers a minimally invasive option to treat the blockages in the arteries supplying your heart. It avoids opening up the chest, avoids general anesthesia, and requires very little recovery time compared to CABG.
In the western countries, this procedure has become like a day care procedure, with patients getting admitted in the morning, observed for a few hours post-procedure, and sent home if ECG is fine and has no symptoms.
Stents are metallic tubes, made of different materials like cobalt, chromium, platinum or a combination of them, depending on the stent platform. Additionally, they also have a drug coating around them to prevent early restenosis at the insertion site. Basically, these stents are a mesh-like tube inserted in the arteries to keep them open with their radial strength.
Nowadays only drug coated stents are used routinely and bare metal stents (non drug coated ones) are almost obsolete and are hardly ever used. Various companies both Indian and International ones manufacture stents. All these stents have their own advantages and drawbacks, so it is prudent to talk to your cardiologist regarding the stent they would be choosing in the angioplasty.
If you have an acute pain in your chest, it is better to reach your closest hospital where there is a facility for doing the angioplasty procedure. If not urgent, you could go to any cardiologist and hospital as per your convenience.
