
Medically Reviewed By Dr. Meghav Shah Updated on December 02, 2024
Pulmonary thromboembolism or PTE is sometimes a life threatening condition in which there is thrombus i.e. blood clots lodged in the pulmonary arteries, i.e. the arteries which supply the lungs. It can be life threatening because these clots can impede the forward flow of blood in the lungs and subsequently cause decreased oxygen levels in the body. Usually the source of PTE is a thrombus in the vein of the legs, a condition called deep vein thrombosis or DVT. This clot i.e the DVT migrates via the Inferior vena cava into the right sided heart chambers and then gets stuck in the pulmonary arteries as they narrow into their branches. The smaller clots get stuck in the smaller lung arteries, whereas the larger clots get stuck in larger lung arteries, causing more symptoms including risk of sudden death.
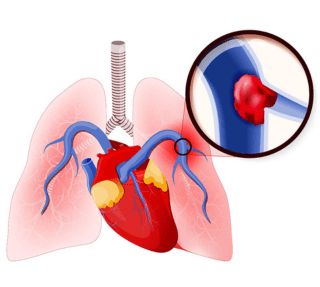
As mentioned, the most common cause of PTE is a clot in the leg veins. This DVT most commonly occurs secondary to immobility. The people who have had a recent surgery which causes decreased leg movements or those who are bedridden due to other conditions are at risk for deep vein thrombosis. Occasionally the PTE can be secondary to air embolism or fat embolism due to trauma and fracture of long bones on the limbs.
Symptoms of PTE can vary depending on the clot burden, the duration of the disease and the amount of lung involved. Patients may be occasionally asymptomatic. Most common symptoms include -
Depending on the symptoms of the patient and the clot burden, the treatment plan is decided.
Medical Management
Blood thinners or anticoagulants - these are started to prevent further clot formations. These can be injectables in the form of heparin or tablets in the form of warfarin or DOAC (directly acting oral anticoagulants) like dabigatran, apixaban, edoxaban or rivaroxaban.
Thrombolytics
These injections are given for life threatening PTE. These medications help in lysing i.e dissolving the formed clots. Thrombolysis is similar to the treatment done for heart attacks and the injections that can be used are tenecteplase or reteplase and occasionally streptokinase.
Surgical Procedures
Catheter directed thrombolysis - can be done when there is great thrombus burden and some risk for bleeding. The advantage of it is that the injections are given directly into the arteries of the lungs where the clot is, via the catheters that are passed through the groins vessels.
Mechanical thrombectomy - this can remove clots from the lung arteries directly via special catheters that can suck out the clots.
IVC filter - this can be occasionally placed if the burden of DVT in the legs is high and the patient cannot take blood thinners because the risk of bleeding is high or has to undergo some major surgeries in the immediate future.
Complications if not treated
As mentioned previously, if not treated promptly, this condition can be life threatening. If untreated it can also cause long term issues like development of pulmonary hypertension which can cause fatigability or worsening shortness of breath and swelling over the feet. This can cause severe impairment of the activities of daily living and can also decrease life expectancy.