
Medically Reviewed By Dr. Meghav Shah Updated on November 28, 2024
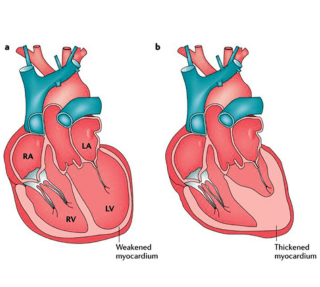
Heart failure is a condition in which the pumping mechanism of the heart is not proper in the form of either reducing pumping capacity or inadequate filling of the heart chambers. Due to this impaired pumping mechanism of the heart, there is fluid build up in the lungs & feet and there is reduced forward flow of blood in the circulation, which are the reasons for the symptoms of heart failure.
Depending on the severity of heart failure, the symptoms vary
In the early stages, there is shortness of breath or fatigue on exertion, then as the heart failure severity worsens, there is shortness of breath on minimal exertion, with feeling short of breath while lying flat on bed too. Initially there is only mild pedal edema or swelling over the ankles, but once heart failure worsens, swelling can extend up to the thighs and genital areas, occasionally in the abdomen too. In most cases of significant heart failure, patients can have irregular heart rate and pulse in the form of atrial fibrillation.
Importance of recognizing symptoms early
It is very important to recognize symptoms of heart failure in the earlier stages as around only 50% of patients survive in 5 years time. Also, early recognition is needed to curtail symptoms and prevent further worsening of impaired heart functioning, by giving timely medications and to treat the underlying cause of heart failure.
Left-sided Heart Failure
It is a condition in which the left ventricle of the heart is not functioning well in the form of its reduced ejection fraction i.e. pump failure or impaired relaxation i.e. diastolic dysfunction. Most common reason for left sided heart failure is coronary artery disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus and age.
Right-sided Heart Failure
It is a condition in which the right ventricle of the heart is not functioning well in the form of reduced ejection fraction i.e drop in the systolic contraction. Most common reason for right sided failure is left sided heart failure and is sometimes secondary to other lung conditions or connective tissue disorders.
Heart failure can also be divided into -
HFrEF - i.e. heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, i.e. LVEF (Left ventricular ejection fraction) is less than 40%.
HFpEF - i.e. heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, i.e. LVEF > 50%
Stage A: High risk of developing heart failure. In this stage, the patient has the risk factors for heart failure, but does not have heart failure per se.
Stage B: Asymptomatic heart failure. In this stage, the patient has signs of heart failure or imaging guided diagnosis of heart failure but is not symptomatic for the same.
Stage C: Symptomatic heart failure. In this stage, the patient has signs and also symptoms of heart failure in the form of shortness of breath or swelling over the feet.
Stage D: Advanced heart failure. In this stage, the patient has florid signs and symptoms of heart failure and despite medications, patient has curtailed quality of life. In these cases, mechanical treatment of heart failure in the form of LVAD (Left ventricular assist devices), etc. may be needed.
Medications
Surgical Options
Lifestyle Modifications
Device Therapy
Heart failure is an understated and under-reported cause of morbidity and mortality. There is a delay in identification of heart failure and when diagnosed very few people are on appropriate medications for the same. Due to all these reasons, it is a major cause of death worldwide. It is pertinent to have regular follow up with the physician for patients having heart failure as they regularly need modifications of medicines and regular blood check ups.
Heart failure and heart attack are both global leaders for cause of death not only in elderly population, but it is also a major cause of mortality in middle and now also younger age groups. Thus it is necessary to prevent these conditions with healthy daily living in the form of a good balanced diet and physical activities. Once diagnosed it has to be treated pro actively and needs lifelong management for the same. Remember prevention is always better than cure.