
Normally, the heart has 4 valves, namely the mitral, aortic, tricuspid and pulmonary valves. These essentially allow smooth forward flow in the circulation of blood and prevent back leaking when functioning normally.
The mitral valve prevents normal passage between the left atria (upper chamber) into the left ventricle (lower chamber). Similarly, the tricuspid valve helps in the passage of blood between the upper and lower chambers on the right side of the heart. The aortic valve helps in passage of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta and eventually into the entire body. The pulmonary valve helps in the passage of blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery i.e. in the lungs.
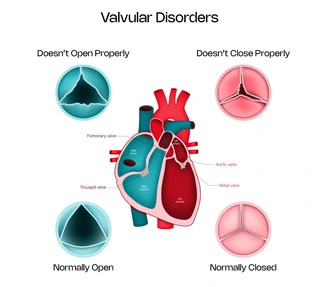
Thus these valves essentially help maintain forward flow of blood and prevent back leak. Thus, any abnormality in it, can prevent the smooth circulation of blood flow in the heart, leading to varied symptoms. Valvular stenosis is a condition where there is impaired opening of the valve, which prevents normal forward flow and valvular regurgitation is a condition where there is impaired closing of the valve, which causes leak or backflow of the blood through the valve.
We will describe these common heart valvular abnormalities and their treatment in this section
This is a condition causing narrowing or impaired opening of the aortic valve, i.e. the valve responsible for transfer of blood from the left ventricle into the aorta. Thus there is less amount of blood going into the body in circulation. It is a common disorder in the elderly and affects 1 in 8 people over 75 years of age.
Causes
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Medical Management - Not much in terms of medications can relieve the symptoms secondary to this condition.
Surgical - TAVR or TAVI - Transcatheter aortic valve replacement or implantation is the preferred choice for patients having severe stenosis especially in patients older than 60 years of age. It is done like angiography through the groins arteries with minimal anesthesia and patients can go home in 2 days time.
Surgical AVR - It is a conventional surgery i.e. open heart surgery especially done for younger patients. It could be with a metallic or tissue valve.
Complications
If untreated, it can cause worsening of symptoms, impaired quality of life, drop in the functioning of the heart pump and also predispose to sudden cardiac death.
This is a condition causing narrowing or impaired opening of the mitral valve, i.e. the valve responsible for transfer of blood from the left atria into the ventricle. Thus there is less amount of blood going into the body in circulation. It is a common disorder in the young and middle aged, especially in the rural parts of India.
Causes
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Medical management - Diuretics (water tablets) and beta blockers are the main treatments for the condition.
Balloon mitral valvotomy (BMV) - It is the preferred choice for patients having severe stenosis if feasible. It is done like angiography through the veins in the groins with minimal anesthesia and patients can go home in 2 days time.
Surgical MVR - It is a conventional surgery i.e. open heart surgery if BMV is not possible. It could be with a metallic or tissue valve. Occasionally, surgeons can also prefer doing open mitral valvotomy (OMV) in some cases.
Complications
If untreated, it can cause worsening of symptoms, impaired quality of life and once right heart failure develops, it can cause steep worsening in the symptoms. If clot forms in the left atria, then can cause stroke or other embolic events.
This is a condition causing leaking of the mitral valve, i.e. the valve responsible for transfer of blood from the left atria into the ventricle. Thus during the left ventricular contraction, there is backflow of blood into the atria because of the mitral valve leak.
Causes
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Medical Management - Diuretics or water tablets can be given. Occasionally, rate controlling medicines can be given in some cases.
TEER - Transcatheter edge to edge repair is the preferred choice for patients having severe regurgitation if feasible, especially in elderly populations. It is done like angiography through the veins in the groins with minimal anesthesia and patients can go home in 2 days time.
Surgical MVR - It is a conventional surgery i.e. open heart surgery if TEER is not possible. It could be with a metallic or tissue valve. Occasionally, surgeons can also prefer doing open mitral valve repair in some cases.
Complications
If untreated, it can cause worsening of symptoms, impaired quality of life and once the left ventricular function drops, it can cause steep worsening in the symptoms. If clot forms in the left atria, then can cause stroke or other embolic events.
This is a condition causing leaking of the tricuspid valve, i.e. the valve responsible for transfer of blood from the right atria into the ventricle. Thus during the right ventricular contraction, there is backflow of blood into the atria because of the tricuspid valve leak.
Causes
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Medical Management - Diuretics or water tablets can be given. Occasionally, rate controlling medicines can be given in some cases.
TEER - Transcatheter edge to edge repair is the preferred choice for patients having severe regurgitation if feasible, especially in elderly populations. It is done like angiography through the veins in the groins with minimal anesthesia and patients can go home in 2 days time.
Occasionally, tricuspid valve replacement can also be done via the groins in some cases. Implanting valves in the vena cavas can also be done to contain the regurgitation into the atria and not transmitting the overload in the abdomen and neck veins.
Surgical TVR - It is an uncommonly done surgery i.e. open heart surgery if TEER is not possible. It is usually done with a tissue valve. More often, surgeons prefer doing open tricuspid valve repair in some cases along with the treatment of other valves.
Complications
If untreated, it can cause worsening of symptoms, impaired quality of life and once the right ventricular function drops, it can cause steep worsening in the symptoms.
This is a condition causing narrowing or impaired opening of the pulmonary valve, i.e. the valve responsible for transfer of blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery. Thus there is less amount of blood going into the lungs.
Causes
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Medical Management - Not much in terms of medications can relieve the symptoms secondary to this condition.
BPV - Transcatheter balloon pulmonary valvotomy is the preferred choice for patients having severe stenosis. It is done like angiography through the groins with minimal anesthesia and patients can go home in 2 days time.
Surgical - Pulmonary valve repair is a conventional surgery i.e. open heart surgery in exceptional cases where balloon procedure is not possible.
Complications
If untreated, it can cause worsening of symptoms, impaired quality of life and also predisposes occasionally to sudden cardiac death.
This is a condition causing leaking of the pulmonary valve, i.e. the valve responsible for transfer of blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery. Thus after the right ventricular contraction, there is backflow of blood into the ventricle, when it relaxes because of the pulmonary valve leak.
Causes
Symptoms
Diagnosis
Treatment
Medical management - Not much in terms of medications can relieve the symptoms secondary to this condition.
PPVR - Percutaneous pulmonary valve replacement or implantation is the preferred choice for patients having severe regurgitation. It is done like angiography through the groins veins with minimal anesthesia and patients can go home in 2 days time.
Surgical - Pulmonary valve repair is a conventional surgery i.e. open heart surgery that can be done if percutaneous procedure is not possible.
Complications
If untreated, it can cause worsening of symptoms, impaired quality of life and also predispose to sudden cardiac death.
